
Music Dictionary/M
Choose the letter which begins musical term that you would like to learn about:
MAbbreviation for mano or main, meaning hand.
M.M. Abbreviation for Maezel's Metronome.
Ma
But. Used with other words, e.g. lento ma non troppo, slow but
not too slowly.
Maggiore Major, referring to mode.
MaestosoMajestically.
Main Hand.
MajorThe designation for certain intervals and scale. A key based
on a major scale is called a major key. The pattern for the
major scale is:
| whole |
whole |
half
|
whole |
whole |
whole
|
half |
| step |
step |
step
|
step |
step |
step
|
step |
Major chordA triad composed of a root, major third, and perfect fifth.
Major intervalsMajor intervals are from the tonic to the second, third, and perfect sixth and seventh degress as they occur in the major scale. Any minor interval enlarged by one semitone becomes a major interval.
Major Locrian ScaleSee Scales and chords.
MancandoFading away
MarcatoEmphasized, heavily accented.
MeasureA group of beats containing a primary accent and one or more
secondary accents, indicated by the placement of bar lines on
the staff. The space between two bar lines.
MedesimoThe same.
MediantThe third degree of the major of minor scale. The triad built
on this degree is labeled iii in the major scale, III in the natural minor scale, and III+ in the harmonic minor scale.
MedievalThe period prior to the Renaissance, c. 500-1450, marking the
music of the early Christian church.
MelodyIn general, a succession of musical tones. It represents the
linear or horizontal aspect of music.
MenoLess.
Meno mossoLess motion.
MeterThe structure of notes in a regular pattern of accented and
unaccented beats within a measure, indicated at the beginning
of a composition by a meter signature.
Meter signature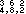 The numbers placed at the beginning of a composition to indicate
the meter of the music. The upper
number indicates the beats in a measure; the lower number tells
what kind of a note will receive one beat. This is sometimes known as a Time Signature.
The numbers placed at the beginning of a composition to indicate
the meter of the music. The upper
number indicates the beats in a measure; the lower number tells
what kind of a note will receive one beat. This is sometimes known as a Time Signature.
Metronome  Invented by Maelzel in 1816, the instrument is used to indicate
the exact tempo of a composition. An indication such as M.M.
60 indicates that the pendulum, with a weight at the bottom, makes
60 beats per minute. A slider is moved up and down the pendulum
to decrease and increase the tempo. M.M.
Invented by Maelzel in 1816, the instrument is used to indicate
the exact tempo of a composition. An indication such as M.M.
60 indicates that the pendulum, with a weight at the bottom, makes
60 beats per minute. A slider is moved up and down the pendulum
to decrease and increase the tempo. M.M. 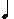 =80 means that the time value of a quarter note is the equivalent
of one pendulum beat when the slider is set at 80.
=80 means that the time value of a quarter note is the equivalent
of one pendulum beat when the slider is set at 80.
MezzoHalf, Medium
Mezzo forte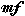 Medium loud.
Medium loud.
Mezzo piano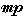 Medium soft.
Medium soft.
Mi In solmization, the third degree of the major scale.
Middle AgesEuropean historical period between roughly A.D. 500 and 1450. More about this time period.
Middle CThe note C in the middle of the Grand staff, and near the middle
of the piano.
MinorThe designation for certain intervals and scales. A key based
on a minor scale is called a minor key. The three types of minor
scales include natural, harmonic, and melodic, which is used infrequently
in choral music. The patterns for natural and harmonic scales
are:
|
natural:
| whole |
half |
whole
| whole |
half |
whole
| whole |
|
|
|
step
|
step |
step |
step
| step |
step |
step
| |
|
harmonic:
| whole |
half |
whole
| whole |
whole | 1-1/2
| half |
|
|
|
step
| step |
step |
step
| step |
steps |
step
| |
melodic:
|
(ascending):
| whole |
half |
whole
| whole |
whole |
whole
| half |
|
|
|
step
| step |
step |
step
| step |
step |
step
| |
|
(descending):
| whole |
whole |
half
| whole |
whole |
half
| whole |
|
|
| |
step
| step |
step |
step
| step |
step |
step
| |
Misterioso Mysteriously.
Mit With.
Mode Any scalewise arrangement of pitches; more generally, the term
refers to the patterns upon which medieval music was structured,
the patterns which preceded the development of major and minor
scales and tonality.
ModeratoModerate speed.
ModernMusic written in the Twentieth century or contempory music.
ModulationThe process of changing from one key to another within a composition.
MoltoVery. Used with other terms, e.g. molto allegro.
Mordent"Biting." An ornament consisting of an alteration
(once or twice) of the written note by playing the one immediately
below it (lower mordent), or above it (upper, or inverted, mordent)
and then playing the note again.
MorendoGradually decreasing in volume; dying away.
MossoRapid. Meno mosso, less rapid. Piu mosso, more rapid.
MotiveA short melodic or rhythmic pattern.
MotoMotion. Con moto, with motion.
Movable DoGenerally any system of solmization so designed that the syllables can be used in transposition to any key; "Do" remaining as the tonal center, regardless of key.
MusicThe organization of sounds with some degree of rhythm, melody,
and harmony.
Music theoryThe study of how music is put together.
Definitions and terms excerpted from
Belwin Pocket Dictionary of Music: Music Theory Dictionary
By Dr. William Lee

The Thomas Music Studio
is located
in Beaverton, Oregon
~~

© 2000
All rights reserved.

The numbers placed at the beginning of a composition to indicate the meter of the music. The upper number indicates the beats in a measure; the lower number tells what kind of a note will receive one beat. This is sometimes known as a Time Signature.
Invented by Maelzel in 1816, the instrument is used to indicate the exact tempo of a composition. An indication such as M.M. 60 indicates that the pendulum, with a weight at the bottom, makes 60 beats per minute. A slider is moved up and down the pendulum to decrease and increase the tempo. M.M.
=80 means that the time value of a quarter note is the equivalent of one pendulum beat when the slider is set at 80.
Medium loud.
Medium soft.

